
And here goes the last section in my AZ-500 study guide, the end is coming with:
- Create and configure Key Vault
- Configure access to Key Vault
- Manage certificates, secrets, and keys
- Configure key rotation
- Configure Backup and recovery of certificates, secrets, and keys
Table of Contents
Create and configure Key Vault
Basics
When you create a Key vault, you will the following options and Vault name must only contain alphanumeric characters and dashes and cannot start with a number.

You have Standard and Premium pricing tiers, in example the monthly pricing with one Managed HSM pool will the following and you will only pay for what you use

| Service type | Region | Description | Estimated monthly cost | Estimated upfront cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Key Vault | North Europe | Vault: 1 operations, 1 advanced operations, 1 renewals 1 protected keys, 1 advanced protected keys | 8,72€ | 0,00€ |
| Managed HSM Pools: 1 Standard B1 HSM Pool(s) x 31 Days | 2 263,66€ | |||
| Support | 0,00€ | 0,00€ | ||
| Total | 2 272,38€ | 0,00€ |
Soft delete protection will automatically be enabled on this key vault. This feature allows you to recover or permanently delete a key vault and secrets for the duration of the retention period. This protection applies to the key vault and the secrets stored within the key vault.
To enforce a mandatory retention period and prevent the permanent deletion of key vaults or secrets prior to the retention period elapsing, you can turn on purge protection. When purge protection is enabled, secrets cannot be purged by users or by Microsoft.
The ability to turn off soft delete via the Azure Portal has been deprecated. You can create a new key vault with soft delete off for a limited time using CLI / PowerShell / REST API. The ability to create a key vault with soft delete disabled will be fully deprecated by the end of the year.

Days to retain can be configured to between 7 to 90 days. Once it has been set, it cannot be changed or removed.
Enabling “purge protection” on a key vault is an irreversible action. Once the purge protection property has been set to “true”, it cannot be changed or removed.

Access policy
Virtual machine for deployment specifies whether Azure Virtual Machines are permitted to retrieve certificates stored as secrets from the key vault.
ARM template specifies whether Azure Resource Manager is permitted to retrieve secrets from the key vault.
Azure Disk Encryption permits Disk encryption to retrieve secrets from the vault and unwrap keys.

When you are adding access policy, you will the following options

Access policy permissions
Key vault supports up to 1024 access policy entries, with each entry granting a distinct set of permissions to a particular security principal.
Authorized application settings performs the specified permissions on the User’s or Group’s behalf.

RBAC
But when you enable RBAC you won’t see any options, I will go thru this on the next section.

Networking
Selected networks
You can select Select network in the connectivity methods and add existing Vnet’s and allow Microsoft trusted services to bypass the the firewall

What are Microsoft trusted services?
| Trusted service | Supported usage scenarios |
|---|---|
| Azure Virtual Machines deployment service | Deploy certificates to VMs from customer-managed Key Vault. |
| Azure Resource Manager template deployment service | Pass secure values during deployment. |
| Azure Disk Encryption volume encryption service | Allow access to BitLocker Key (Windows VM) or DM Passphrase (Linux VM), and Key Encryption Key, during virtual machine deployment. This enables Azure Disk Encryption. |
| Azure Backup | Allow backup and restore of relevant keys and secrets during Azure Virtual Machines backup, by using Azure Backup. |
| Exchange Online & SharePoint Online | Allow access to customer key for Azure Storage Service Encryption with Customer Key. |
| Azure Information Protection | Allow access to tenant key for Azure Information Protection. |
| Azure App Service | App Service is trusted only for Deploying Azure Web App Certificate through Key Vault, for individual app itself, the outbound IPs can be added in Key Vault's IP-based rules |
| Azure SQL Database | Transparent Data Encryption with Bring Your Own Key support for Azure SQL Database and Azure Synapse Analytics. |
| Azure Database for MySQL | Data encryption for Azure Database for MySQL |
| Azure Database for PostgreSQL Single server | Data encryption for Azure Database for PostgreSQL Single server |
| Azure Storage | Storage Service Encryption using customer-managed keys in Azure Key Vault. |
| Azure Data Lake Store | Encryption of data in Azure Data Lake Store with a customer-managed key. |
| Azure Synapse Analytics | Encryption of data using customer-managed keys in Azure Key Vault |
| Azure Databricks | Fast, easy, and collaborative Apache Sparkbased analytics service |
| Azure API Management | Deploy certificates for Custom Domain from Key Vault using MSI |
| Azure Data Factory | Fetch data store credentials in Key Vault from Data Factory |
| Azure Event Hubs | Allow access to a key vault for customer-managed keys scenario |
| Azure Service Bus | Allow access to a key vault for customer-managed keys scenario |
| Azure Import/Export | Use customer-managed keys in Azure Key Vault for Import/Export service |
| Azure Container Registry | Registry encryption using customer-managed keys |
| Azure Application Gateway | Using Key Vault certificates for HTTPS-enabled listeners |
| Azure Front Door | Using Key Vault certificates for HTTPS |
| Microsoft Purview | Using credentials for source authentication in Microsoft Purview |
| Azure Machine Learning | Secure Azure Machine Learning in a virtual network |
Private endpoints

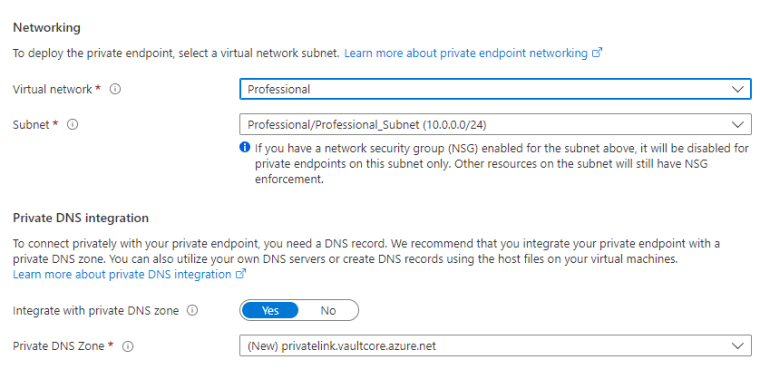
When you start creating a Private endpoint, you will choose a location, name and Target Sub-resource, in this case it will be Vault. Microsoft is using service tags for these. They will allow you to access service under tag and you don’t specify any IP-addresses.

Then you will specify Vnet, subnet and Private DNS. Private DNS will allow the usage with a private DNS name.
If you don’t integrate your endpoint with a DNS zone, you’ll need to create records on either your own DNS server or via host file updates on each virtual machine.
Only private DNS zones in the currently selected subscription with name ‘privatelink.vaultcore.azure.net’ will be shown. Using a private DNS zone in the same resource group as the virtual network is recommended, and if there are no existing zones that meet this criteria, one will be created.
Template
Once you are ready to deploy, you can see the template and easily learn how ARM-templates work. You could also deploy directly from the template page

Or go with manual option

Configure access to Key Vault
Authentication options
- Application-only: The application represents a service principal or managed identity. This identity is the most common scenario for applications that periodically need to access certificates, keys, or secrets from the key vault. For this scenario to work, the
objectIdof the application must be specified in the access policy and theapplicationIdmust not be specified or must benull. - User-only: The user accesses the key vault from any application registered in the tenant. Examples of this type of access include Azure PowerShell and the Azure portal. For this scenario to work, the
objectIdof the user must be specified in the access policy and theapplicationIdmust not be specified or must benull. - Application-plus-user (sometimes referred as compound identity): The user is required to access the key vault from a specific application and the application must use the on-behalf-of authentication (OBO) flow to impersonate the user. For this scenario to work, both
applicationIdandobjectIdmust be specified in the access policy. TheapplicationIdidentifies the required application and theobjectIdidentifies the user. Currently, this option isn’t available for data plane Azure RBAC.
Security principal
A security principal is an object that represents a user, group, service, or application that’s requesting access to Azure resources. Azure assigns a unique object ID to every security principal.
- A user security principal identifies an individual who has a profile in Azure Active Directory.
- A group security principal identifies a set of users created in Azure Active Directory. Any roles or permissions assigned to the group are granted to all of the users within the group.
- A service principal is a type of security principal that identifies an application or service, which is to say, a piece of code rather than a user or group. A service principal’s object ID is known as its client ID and acts like its username. The service principal’s client secret acts like its password.
For applications, there are two ways to obtain a service principal:
- Recommended: enable a system-assigned managed identity for the application.With managed identity, Azure internally manages the application’s service principal and automatically authenticates the application with other Azure services. Managed identity is available for applications deployed to a variety of services.For more information, see the Managed identity overview. Also see Azure services that support managed identity, which links to articles that describe how to enable managed identity for specific services (such as App Service, Azure Functions, Virtual Machines, etc.).
- If you cannot use managed identity, you instead register the application with your Azure AD tenant

How to?
When you open the deployed Key vault you and Access policies, you will see the following
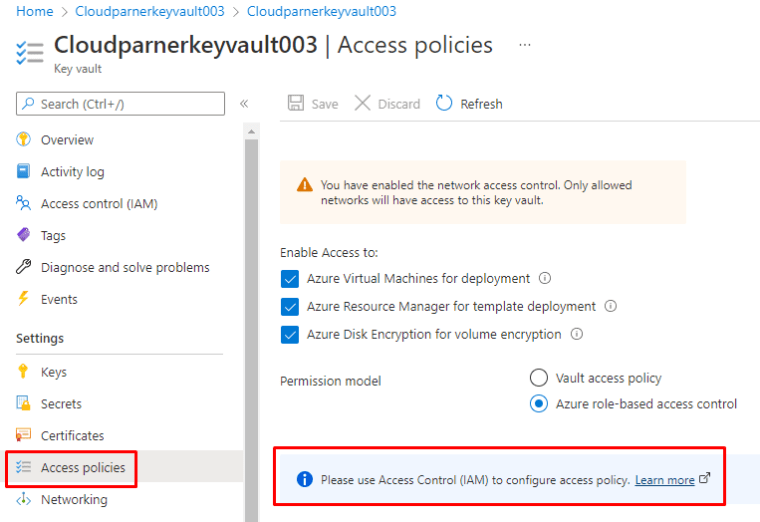
And this is because we have RBAC enabled, so let’s dig to RBAC first
RBAC
You have and options see view Your own access, access for users, groups or Service principals and managed identities.
But also grant access to Key vault ja view all access and what is denied

From View my access you will see the default access your accounts has. My account example has Owner that is Inherited from subscription level and because I have PIM Enabled, there is also User Access Administrator permissions

Different roles

Contributor means Inherited or direct permissions but also Key Vault contributor permissions have this right.
Inherited contributor

Key Vault contributor

And here are the different roles specific to Key vault
| Built-in role | Description | ID |
|---|---|---|
| Key Vault Administrator | Perform all data plane operations on a key vault and all objects in it, including certificates, keys, and secrets. Cannot manage key vault resources or manage role assignments. Only works for key vaults that use the ‘Azure role-based access control’ permission model. | 00482a5a-887f-4fb3-b363-3b7fe8e74483 |
| Key Vault Certificates Officer | Perform any action on the certificates of a key vault, except manage permissions. Only works for key vaults that use the ‘Azure role-based access control’ permission model. | a4417e6f-fecd-4de8-b567-7b0420556985 |
| Key Vault Crypto Officer | Perform any action on the keys of a key vault, except manage permissions. Only works for key vaults that use the ‘Azure role-based access control’ permission model. | 14b46e9e-c2b7-41b4-b07b-48a6ebf60603 |
| Key Vault Crypto Service Encryption User | Read metadata of keys and perform wrap/unwrap operations. Only works for key vaults that use the ‘Azure role-based access control’ permission model. | e147488a-f6f5-4113-8e2d-b22465e65bf6 |
| Key Vault Crypto User | Perform cryptographic operations using keys. Only works for key vaults that use the ‘Azure role-based access control’ permission model. | 12338af0-0e69-4776-bea7-57ae8d297424 |
| Key Vault Reader | Read metadata of key vaults and its certificates, keys, and secrets. Cannot read sensitive values such as secret contents or key material. Only works for key vaults that use the ‘Azure role-based access control’ permission model. | 21090545-7ca7-4776-b22c-e363652d74d2 |
| Key Vault Secrets Officer | Perform any action on the secrets of a key vault, except manage permissions. Only works for key vaults that use the ‘Azure role-based access control’ permission model. | b86a8fe4-44ce-4948-aee5-eccb2c155cd7 |
| Key Vault Secrets User | Read secret contents. Only works for key vaults that use the ‘Azure role-based access control’ permission model. | 4633458b-17de-408a-b874-0445c86b69e6 |
From RBAC your can add user, groups, Service principals and Managed identities

And you can check the access from role assignments

Access policies
Switching to access policies is relatively easy, just go to Access policies and dip the switch. You will get a warning stating that entities will loose access

But note this before changing

If you need to use or just trying out, you will see the following permissions available, you can set different permissions for Keys, Secret or certificate inside the Key vault as long as you remember that granularity isn’t supported, you have to define the access policies to the Key vault at top level.
With RBAC you have possibility to define access for item level.

And Microsoft also suggests you to use RBAC based permissions model instead of policies
Access policy templates to Azure roles mapping
| Access policy template | Operations | Azure role |
|---|---|---|
| Key, Secret, Certificate Management | Keys: all operations Certificates: all operations Secrets: all operations | Key Vault Administrator |
| Key & Secret Management | Keys: all operations Secrets: all operations | Key Vault Crypto Officer Key Vault Secrets Officer |
| Secret & Certificate Management | Certificates: all operations Secrets: all operations | Key Vault Certificates Officer Key Vault Secrets Officer |
| Key Management | Keys: all operations | Key Vault Crypto Officer |
| Secret Management | Secrets: all operations | Key Vault Secrets Officer |
| Certificate Management | Certificates: all operations | Key Vault Certificates Officer |
| SQL Server Connector | Keys: get, list, wrap key, unwrap key | Key Vault Crypto Service Encryption User |
| Azure Data Lake Storage or Azure Storage | Keys: get, list, unwrap key | N/A Custom role required |
| Azure Backup | Keys: get, list, backup Secrets: get, list, backup | N/A Custom role required |
| Exchange Online Customer Key | Keys: get, list, wrap key, unwrap key | Key Vault Crypto Service Encryption User |
| Exchange Online Customer Key | Keys: get, list, wrap key, unwrap key | Key Vault Crypto Service Encryption User |
| Azure Information BYOK | Keys: get, decrypt, sign | N/A Custom role required |
Assignment scopes mapping
Azure RBAC for Key Vault allows roles assignment at following scopes:
- Management group
- Subscription
- Resource group
- Key Vault resource
- Individual key, secret, and certificate
Access policy to RBAC migration
There are many differences between Azure RBAC and vault access policy permission model. In order, to avoid outages during migration, below steps are recommended.
- Identify and assign roles: identify built-in roles based on mapping table above and create custom roles when needed. Assign roles at scopes, based on scopes mapping guidance. For more information on how to assign roles to key vault, see Provide access to Key Vault with an Azure role-based access control
- Validate roles assignment: role assignments in Azure RBAC can take several minutes to propagate. For guide how to check role assignments, see List roles assignments at scope
- Configure monitoring and alerting on key vault: it’s important to enable logging and setup alerting for access denied exceptions. For more information, see Monitoring and alerting for Azure Key Vault
- Set Azure role-based access control permission model on Key Vault: enabling Azure RBAC permission model will invalidate all existing access policies. If an error, permission model can be switched back with all existing access policies remaining untouched.
Manage certificates, secrets, and keys
Certificates
Key vault can be used to generate certificates or just store them for safe-keeping.
You an choose similar options than with your own Certification Authority. Validity period (Maximum 1200 months!) to key usage, it’s all there.

You can choose Integrated CAs which are managed by key vault, which include: DigiCert, GlobalSign

Lifetime action

You can see Certificate transparency, wondering what it is?
Key usage

Import a certificate

For a certificate import operation, Azure Key Vault accepts two certificate file formats: PEM and PFX. Although there are PEM files with only the public portion, Key Vault requires and accepts only a PEM or PFX file with a private key.

Secrets

When you create a secret, you will see the option to create a certificate but it isn’t available anymore, it has been moved to certificates page.

The Azure Portal currently only supports single-line secret values. Please use Azure PowerShell to set multi-line values.
From here you can also add Activate and Expiration date. Activation adds NBF and Expiration EXP property to the secret.

When you press create, you will get the following warning

We enabled the network security but didn’t add the Client IP to firewall (Microsoft please add the current client IP automatically to the column!)

Once done, success!

And lastly keys
Generate

Or import

For keys there is an excellent solution called Auto Key rotation which just came Globally available!
Configure (Auto) key rotation
Permissions required
Key Vault key rotation feature requires key management permissions. You can assign a “Key Vault Administrator” role to manage rotation policy and on-demand rotation.
For more information on how to use RBAC permission model and assign Azure roles, see: Use an Azure RBAC to control access to keys, certificates and secrets

Let’s explore the options
You have two different access policy permission models.
RBAC based

Vault Access policy

Policy based on RBAC
You have a Key Vault and will generate a new key and rotation policy to it.

And you will be displayed with the following error.

Go to Access control and add role assigment.

Add Key Vault Administrator

Here you can add Users, Groups, Service principals or even Managed identities.

What are managed identities?
I will choose users for demonstration purposes. You can check your rights from the same pane.

Then back to key rotation.
Now you can enable key rotation. In my example I chose expiration time to 1 year and rotation time for 355 days as there has to be lower than 358 days.

And with policy based permissions model
You have to add “Get Rotation Policy” right.

Go to Access policies and add “Get Rotation Policy”

Go back to keys and you will see the same options for adding Key Rotation.

ARM-template
You can also add Key Rotation to ARM template with the following.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 |
{ "$schema": "https://schema.management.azure.com/schemas/2019-04-01/deploymentTemplate.json#", "contentVersion": "1.0.0.0", "parameters": { "vaultName": { "type": "String", "metadata": { "description": "The name of the key vault to be created." } }, "keyName": { "type": "String", "metadata": { "description": "The name of the key to be created." } }, "rotateTimeAfterCreation": { "defaultValue": "P18M", "type": "String", "metadata": { "description": "Time duration to trigger key rotation. i.e. P30D, P1M, P2Y" } }, "expiryTime": { "defaultValue": "P2Y", "type": "String", "metadata": { "description": "The expiry time for new key version. i.e. P90D, P2M, P3Y" } }, "notifyTime": { "defaultValue": "P30D", "type": "String", "metadata": { "description": "Near expiry event grid notification. i.e. P30D" } } }, "resources": [ { "type": "Microsoft.KeyVault/vaults/keys", "apiVersion": "2021-06-01-preview", "name": "[concat(parameters('vaultName'), '/', parameters('keyName'))]", "location": "[resourceGroup().location]", "properties": { "vaultName": "[parameters('vaultName')]", "kty": "RSA", "rotationPolicy": { "lifetimeActions": [ { "trigger": { "timeAfterCreate": "[parameters('rotateTimeAfterCreation')]", "timeBeforeExpiry": "" }, "action": { "type": "Rotate" } }, { "trigger": { "timeBeforeExpiry": "[parameters('notifyTime')]" }, "action": { "type": "Notify" } } ], "attributes": { "expiryTime": "[parameters('expiryTime')]" } } } } ] } |
Configure Backup and recovery of certificates, secrets, and keys
Prerequisites
To back up a key vault object, you must have:
- Contributor-level or higher permissions on an Azure subscription.
- A primary key vault that contains the secrets you want to back up.
- A secondary key vault where secrets will be restored.
Certificates

Store it in a safe place

Deleting the certificate, ups

Open Deleted certificates

When you have the Soft-Delete enable, it’s easy

Or from backup

Secrets
Again if you have Soft-Delete enabled, it’s quite easy


Or if You have an backup

And restore the backup

Key
Again, similar process. If you have a backup, you can just restore it

And choose the file

and if you have Soft-Delete enabled, just restore it from there. Microsoft really made this easy and consistent, nice job!
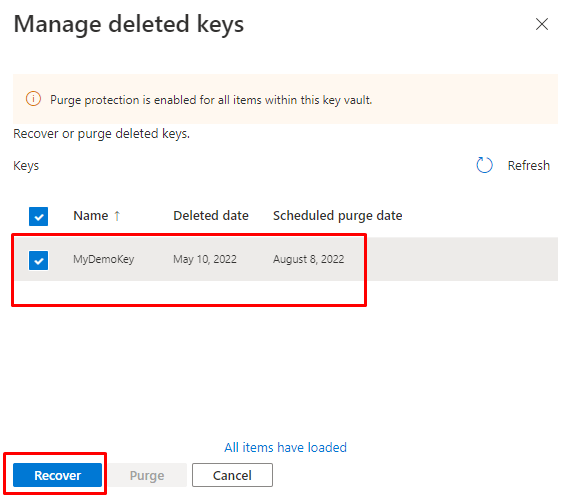
Restoring the whole Key vault
Even restoring a deleted Key vault is possible, if you accidentally deleted a Key vault, it will stay in the recycle bin for 90 days!


What are the limitations for Key Vault?
Key transactions (maximum transactions allowed in 10 seconds, per vault per region1)
| Key type | HSM key CREATE key | HSM key All other transactions | Software key CREATE key | Software key All other transactions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RSA 2,048-bit | 5 | 1,000 | 10 | 2,000 |
| RSA 3,072-bit | 5 | 250 | 10 | 500 |
| RSA 4,096-bit | 5 | 125 | 10 | 250 |
| ECC P-256 | 5 | 1,000 | 10 | 2,000 |
| ECC P-384 | 5 | 1,000 | 10 | 2,000 |
| ECC P-521 | 5 | 1,000 | 10 | 2,000 |
| ECC SECP256K1 | 5 | 1,000 | 10 | 2,000 |
Secrets, managed storage account keys, and vault transactions
| Transactions type | Maximum transactions allowed in 10 seconds, per vault per region1 |
|---|---|
| All transactions | 2,000 |
1 A subscription-wide limit for all transaction types is five times per key vault limit. For example, HSM-other transactions per subscription are limited to 5,000 transactions in 10 seconds per subscription.
Backup keys, secrets, certificates
| Transactions type | Maximum key vault object versions allowed |
|---|---|
| Backup individual key, secret, certfiicate | 500 |
Azure Private Link integration
| Resource | Limit |
|---|---|
| Private endpoints per key vault | 64 |
| Key vaults with private endpoints per subscription | 400 |
Possible use cases for Key vault
SSL certificates for Apps

You can use certificates from Key Vault, which is kinda neat feature.

Customer Managed TDE
How customer-managed TDE works?
For server to be able to use TDE protector stored in AKV for encryption of the DEK, key vault administrator needs to give the following access rights to the server using its unique Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) identity:
- get – for retrieving the public part and properties of the key in the Key Vault
- wrapKey – to be able to protect (encrypt) DEK
- unwrapKey – to be able to unprotect (decrypt) DEK

Requirements for configuring Azure Key Vault
- Key vault and SQL Database/managed instance must belong to the same Azure Active Directory tenant. Cross-tenant key vault and server interactions are not supported. To move resources afterwards, TDE with AKV will have to be reconfigured. Learn more about moving resources.
- Soft-delete and Purge protection features must be enabled on the key vault to protect from data loss due to accidental key (or key vault) deletion.
- Soft-deleted resources are retained for 90 days, unless recovered or purged by the customer. The recover and purge actions have their own permissions associated in a key vault access policy. The Soft-delete feature can be enabled using the Azure portal, PowerShell or Azure CLI.
- Purge protection can be turned on using Azure CLI or PowerShell. When purge protection is enabled, a vault or an object in the deleted state cannot be purged until the retention period has passed. The default retention period is 90 days, but is configurable from 7 to 90 days through the Azure portal.
- Grant the server or managed instance access to the key vault (get, wrapKey, unwrapKey) using its Azure Active Directory identity. When using the Azure portal, the Azure AD identity gets automatically created when the server is created. When using PowerShell or Azure CLI, the Azure AD identity must be explicitly created and should be verified. See Configure TDE with BYOK and Configure TDE with BYOK for SQL Managed Instance for detailed step-by-step instructions when using PowerShell.
- Depending on the permission model of the key vault (access policy or Azure RBAC), key vault access can be granted either by creating an access policy on the key vault, or by creating a new Azure RBAC role assignment with the role Key Vault Crypto Service Encryption User.
- When using firewall with AKV, you must enable option Allow trusted Microsoft services to bypass the firewall.
These are just couple of examples for your reference!
HSM
What is Hardware Security Module (HSM)
In order to understand Key Vault, we need to understand HSM.
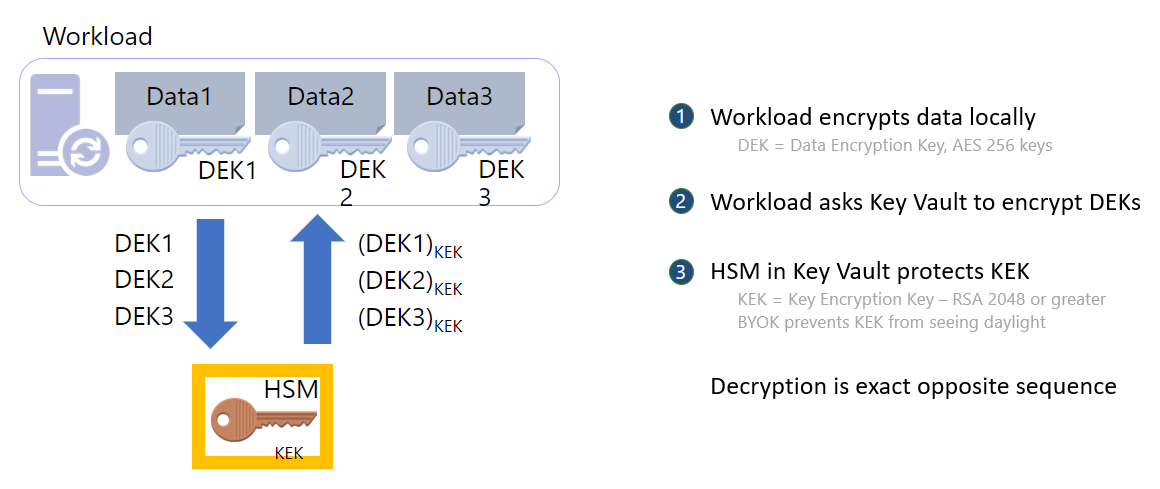
HSM is a tamper proof hardware device which is specifically designed to securely store cryptographic keys.
- Keys can be generated within HSM, or they can also be securely imported to HSM.
- The keys which are generated or imported to HSM never come out of HSM boundary, and it is not possible to extract / decrypt those keys using any tool or program. Although those keys cannot be decrypted, but those keys can be used to encrypt and decrypt other keys and secrets which are stored within Key Vault.
You don’t find Manage HSM inside Azure portal, you can provisioning it with PowerShell, Azure CLI or ARM.

Azure Dedicated HSM is not a good fit for the following type of scenario:
Microsoft cloud services that support encryption with customer-managed keys , such as Azure Information Protection, Azure Disk Encryption, Azure Data Lake Store, Azure Storage, Azure SQL Database, and Customer Key for Office 365.
Microsoft has Azure dedicated HSM but that will be removed and the next generation version is.
Azure Key Vault Managed HSM
Azure SQL now supports using a RSA key stored in a Managed HSM as TDE Protector. Azure Key Vault Managed HSM is a fully managed, highly available, single-tenant, standards-compliant cloud service that enables you to safeguard cryptographic keys for your cloud applications, using FIPS 140-2 Level 3 validated HSMs. Managed HSMs use Marvell LiquidSecurity HSM adapters.
How to enable?
Just choose the premium pricing and your done.

Methods and endpoints
| Resource type | Key protection methods | Data-plane endpoint base URL |
|---|---|---|
| Vaults | Software-protected and HSM-protected (with Premium SKU) | https://{vault-name}.vault.azure.net |
| Managed HSMs | HSM-protected | https://{hsm-name}.managedhsm.azure.net |
Pricing for Managed HSM
| Standard | Premium | |
|---|---|---|
| RSA 2048-bit keys | N/A | €0.863 per key per month1 + €0.026/10,000 transactions |
| Advanced key types1— RSA 3072-bit, RSA 4096-bit, and Elliptic-Curve Cryptography (ECC) keys | N/A | First 250 keys€4.312 per key per monthFrom 251 – 1500 keys€2.156 per key per monthFrom 1501 – 4000 keys€0.777 per key per month4001+ keys€0.345 per key per month+ €0.130/10,000 transactions |
Here is an excellent article on Managed HSM by Nicholas Kondamudi
Things to remember
What are Microsoft trusted services, maybe not needed for the exam but nice to know!
The ability to turn off soft delete via the Azure Portal has been deprecated. You can create a new key vault with soft delete off for a limited time using CLI / PowerShell / REST API. The ability to create a key vault with soft delete disabled will be fully deprecated by the end of the year.
Why to choose RBAC over Access policies and how to migrate?
Key Vault authentication options, when to use what?
Different roles for Key vault and Access policy templates to Azure roles mappings
Process of Access policy to RBAC migration
How to make Key vault secure with Networking restrictions.
How to use Key auto-rotation, excellent excellent feature!
And the limitations for Key vault
Integration with HSM to store keys securely
Thank you!
For this last post I will like to thank You all for reading and supporting. All the feedback is welcome from my audience because you are the ones that this these post are for. Raising the community, because the community raised me!
and then moving to the next one, still didn’t decide which one, could be one of the following.


In the meantime you can book time with me for MVP or technical mentoring, many have already done so. See here for more info.
#Azure #Identity #Security #sharingiscaring #Neverstoplearning
Link to main post



 RSS - Posts
RSS - Posts